Antimony Mining Process
Antimony ore beneficiation usually adopts gravity separation and flotation as a combined process. The specific gravity of antimony ore is much greater than that of gangue. It is separated by gravity separation to pre-enrich the low-grade ore. The antimony ore, after gravity separation, is then purified by flotation.
Antimony Ore Beneficiation
Introduction
About Antimony Ore
Antimony ore refers to rocks or minerals that contain significant amounts of antimony, a chemical element with the symbol Sb and atomic number 51.
Existing Form: ① Natural compounds and intermetallic compounds, such as natural antimony, arsenic antimony ore; ② Sulfides and sulfide salts, such as stibnite, pyro-copper antimony ore, sulfide antimonite, stibnite, chertite, and wheel ore, sulfur antimony lead ore, brittle sulfur antimony lead ore, sulfide antimony lead ore, sulfur antimony silver ore, stibnite silver ore, stibnite lead-silver ore, sulfur mercury antimony ore, sulfur antimony ore, etc.; ③Halide or containing Halides, such as antimonite lead ore, etc.; ④ oxides, such as antimony, yellow antimony, antimony ocher, antimonyite, hydroantimonyite, antimonite, etc.
Common Antimony Ores: Stibnite (antimony sulfide), quartz antimony ore, antimony arsenite, heptavalent antimony ore (antimony oxide), and stibnite (antimony sulfide oxide), etc.
Industrial Use: Mainly used in alloy manufacturing, pyrotechnics, semiconductor manufacturing, and other fields.
Distribution: Larger antimony mineral deposits are distributed in countries such as China, Russia, Bolivia, South Africa, and Mexico.
Mineral Processing
Antimony Ore Beneficiation Methods
The antimony ore beneficiation methods mainly include manual separation, gravity separation, flotation, and other methods. Select the beneficiation process of a specific ore based on the physical and chemical properties of the ore type (natural type and industrial type), mineral composition, structural structure, and process particle size of useful minerals. In addition, consider the content of valuable components in the ore, such as height and antimony metallurgical technology requirements.
Manual Separation
The particle size range generally suitable for the manual separation method is between 28 and 150mm. It is usually completed on the belt conveyor of the mineral processing plant, but some mines complete simple manual selection operations in the pit or at the pit mouth. The massive antimony concentrate tungsten obtained by manual separation contains more than 7% antimony, which can then be smelted to produce raw antimony. It should be noted that in order to improve the efficiency of manual separation, the ore should be washed to remove sludge impurities before beneficiation. The hand-selected tailings enter the gravity selection process again.
Gravity Separation
Gravity separation is one of the most economical, ideal, and effective antimony beneficiation methods. It can also be used as a pre-enrichment operation for flotation, reducing the burden on grinding equipment and improving the efficiency of the process flow. Due to the characteristics of high density and coarse particles of antimony ore, it can be separated from gangue materials through gravity separation. Common stibnite, yellow antimony, red antimony, and antimony are all suitable for gravity separation. The primary condition for gravity beneficiation is monomer dissociation. For antimony ore beneficiation, the degree of monomer dissociation between antimony ore and waste rock directly affects the effect and beneficiation index of gravity separation. It is necessary to crush or even grind the antimony ore to break the conjoined structure and dissociate the antimony ore from the waste rock monomer. The higher the degree of monomer dissociation, the higher the beneficiation effect and recovery. The investment in gravity separation is relatively small, and it is still a mineral processing method that many mineral processing plants are willing to adopt.
Flotation
Flotation is a commonly used method for antimony beneficiation. The types of ores suitable for treatment include antimony sulfide ore, sulfide-oxidation mixed antimony ore, stibnite, tungsten-antimony-gold polymetallic sulfide ore, antimony-arsenic-gold sulfide ore, and tin-lead Antimony-zinc polymetallic sulfide ore, antimony-lead-zinc-mercury polymetallic sulfide ore, arsenic-antimony-gold polymetallic sulfide ore, etc.
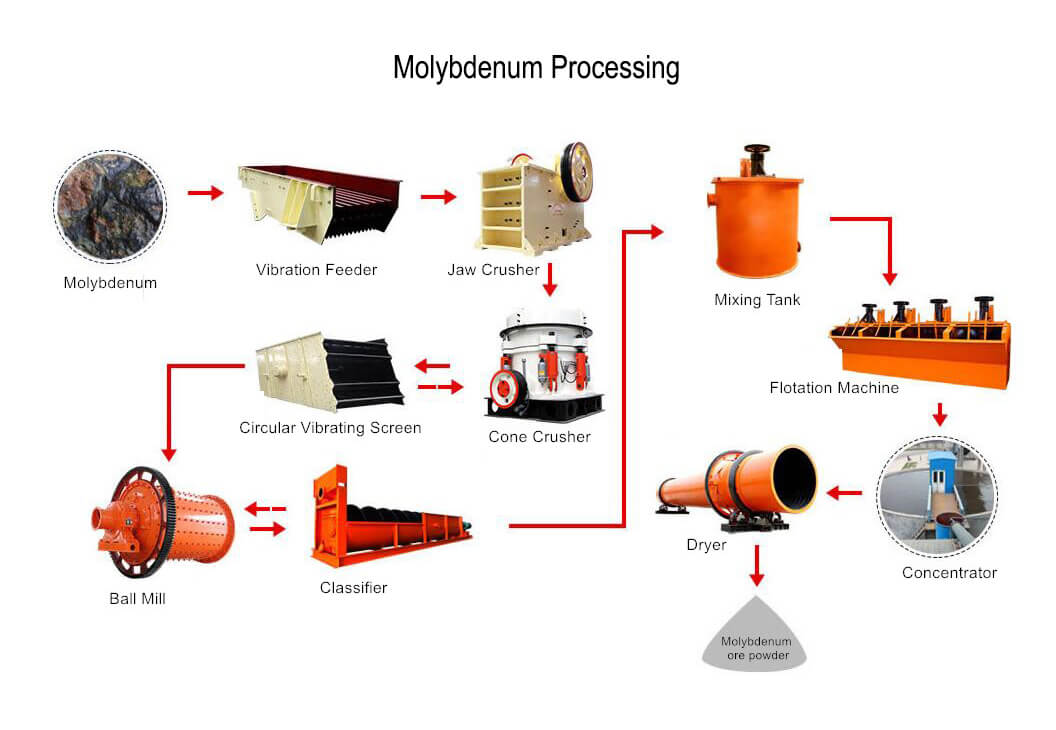
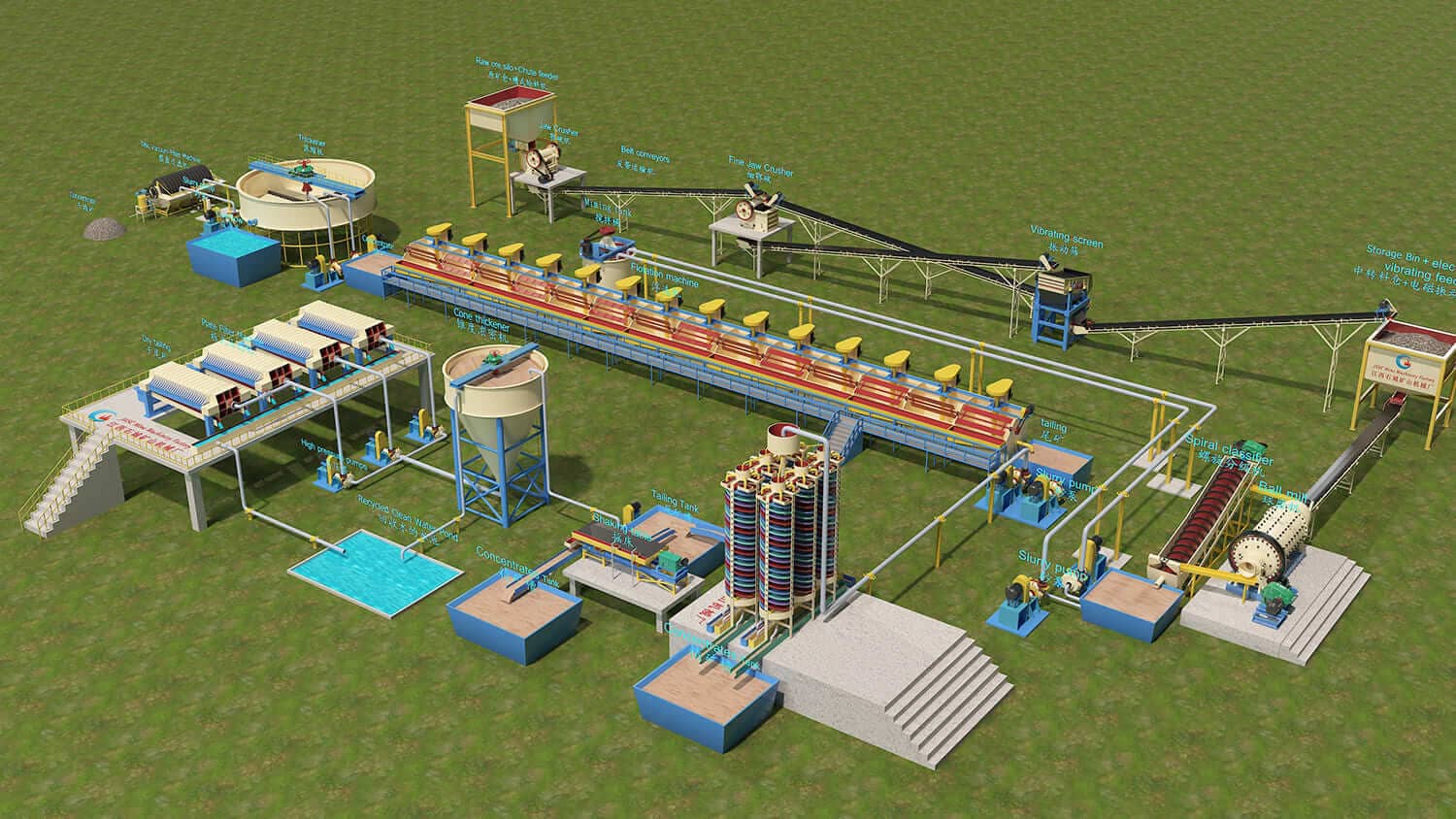
Antimony Ore Mining Process
300TPD Sulfide Antimony Flotation Process Plant
- The chute feeder is for feeding the stones to the jaw crusher automatically.
- The jaw crusher crushes the big stones to small, then to the fine jaw crusher.
- The fine jaw crusher crushes the output from the jaw crusher to make the stones into fine sands.
- The vibration screen is for sieving more than 20mm back to the fine jaw crusher and 0-20mm to the storage bin.
- The storage bin+electromagnetic feeder automatically feeds the materials to the ball mill.
- The ball mill grills the fine sands to 0-1mm, combined with the spiral classifier, to ensure the final product’s size is 0-0.074mm.
- The No.1 slurry pump transports the overflow from the spiral classifier to the flotation machine.
- The flotation machine is used to get the antimony concentrate with chemicals.
- The antimony concentrate of the flotation machine will go to the thickener and then to the disc vacuum filter machine to get the final products dry.
- The tailing of the flotation machine will pump to the spiral chute to recover the antimony, and the antimony concentrated from the spiral chute will go to the shaking table again.
- The tailing of the spiral chute and shaking table will pump to the cone thickener and then to the plate filter machines to recycle the water from the tailings.