Home » Equipment » Flotation Equipment » Mining Mixing Tank
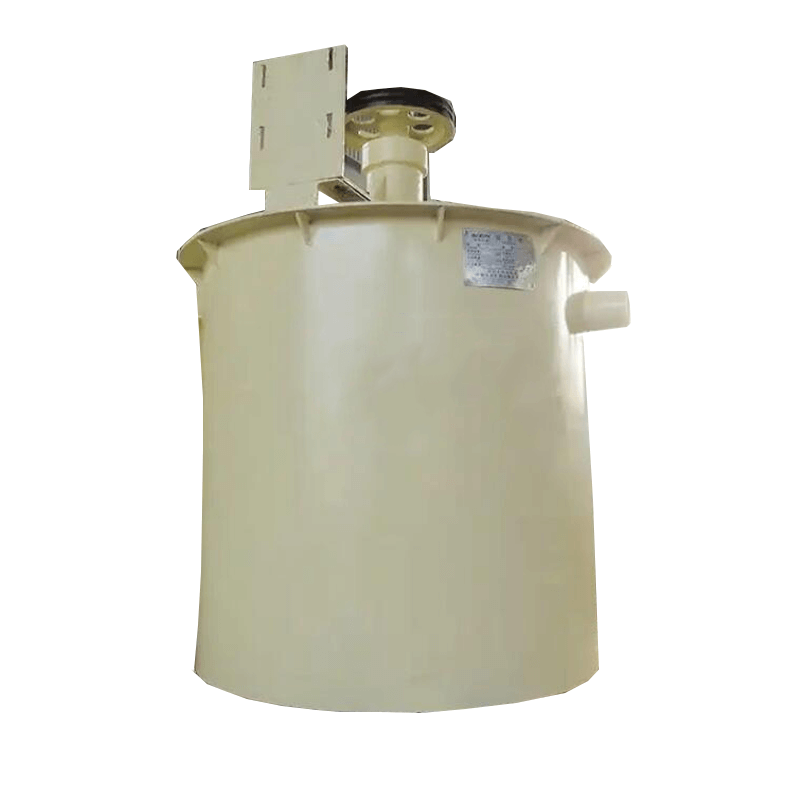

Mining Mixing Tank
The mining mixing tank is a specialized piece of equipment used for mixing slurry before flotation operations. It uses mechanical agitation to thoroughly mix the slurry with reagents, making it suitable for pre-processing of both metallic and non-metallic minerals.
Capacity: 0.58-30 m3
Tank Diameter: 1-3.5 m
Impeller Diameter: 0.24-0.85 m
Power: 1.1-30 kW
Applicable materials: Metal and non-metal mineral processing, rare and precious metals, certain chemical raw materials, etc.
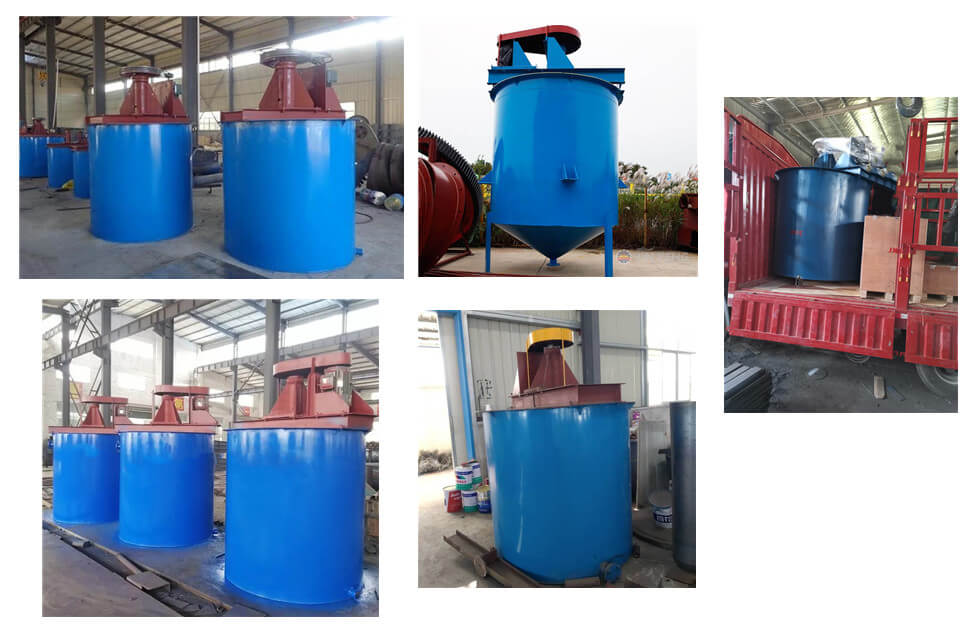

Mixing Tank Overview
A mining mixing tank, or a blending or agitation tank, is a container used in the mineral processing industry to mix various components, such as ore, chemicals, and water, to create a homogeneous slurry. This slurry is crucial in many mining processes, including leaching, precipitation, flotation, and hydrometallurgical processes. The tank facilitates the efficient mixing of different materials to achieve the desired chemical reactions and separation of valuable minerals from the ore.
The mixing tank is suitable for various metal ores and is mainly used for stirring before flotation to mix the reagent and the slurry thoroughly. It can also be used for stirring other non-metallic minerals. It is suitable for fixed components with a concentration of no more than 30% (calculated by weight) and a particle size of less than 1mm.
In the mining industry, mixing tanks play a crucial role in various mineral processing operations, where the efficient blending and mixing of materials are essential for extracting valuable minerals from ores. Here are the specific applications and features of mixing tanks in mining:
Applications of Mining Mixing Tank
- Leaching Processes: Mixing tanks are used where chemicals are mixed with crushed ore to extract valuable minerals. Standard leaching methods include cyanide leaching for gold and silver extraction.
- Flotation: In flotation processes, mixing tanks create a slurry of finely ground ore, water, and flotation reagents. The agitated slurry is then introduced to flotation cells, where mineral particles are separated based on their hydrophobicity.
- Hydrometallurgical Processes: Mixing tanks are employed in various hydrometallurgical processes, such as solvent extraction and precipitation, where the goal is to separate and recover specific metals from the ore.
- Solid-Liquid Separation: After chemical processes, mixing tanks may be involved in solid-liquid separation steps to remove impurities and concentrate valuable minerals.
- Mineral Beneficiation: Mixing tanks are used in the beneficiation process to create a well-mixed slurry of ore, water, and chemicals, ensuring optimal downstream separation and processing conditions.
- Tailings Management: Mixing tanks can be used to prepare and manage tailings, which are the residues left after extracting valuable minerals. Tailings may undergo mixing for proper disposal or to recover residual metals.
Features
- Agitators
Agitators, which can be paddle, propeller, or impeller types, are essential for adequately mixing ore, water, and chemicals within the tank. - Material Construction
Tanks are typically constructed from materials that can withstand corrosive chemicals and abrasive ores, such as stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant alloys.

Abrasion Resistance
Features like abrasion-resistant coatings or lining are incorporated to withstand the wear and tear caused by abrasive materials during mixing.Temperature and Pressure Control
Some processes in mining may involve high temperatures or pressures, so mixing tanks may include controls for these conditions.Baffles
Internal baffles are used to improve mixing efficiency by controlling the flow patterns within the tank.Inlet and Outlet Ports
Mixing tanks are designed with ports for the controlled introduction of materials and the removal of the processed slurry.
Advantages
Mixing Tank Advantages
- Acid-resistant, alkali-resistant, lightweight, and anti-corrosion.
- Small and medium-sized mineral processing enterprises have low costs and little speculation.
- Simple and convenient operation, economical and practical.
- Compact structure, good sealing, and equipped with an ash barrier at the feed inlet to prevent water mist from crossing back.
- Stir evenly; the stirring blades are fan-shaped, and the contact area with the medium is large during stirring.
- Multiple rows of nozzles, the water volume is uniform and adjustable.
- The remaining ash rate is low, and the setting of the watershed at the bottom of the box ensures that there are no dead corners in the equipment.
- The mining mixing drum equipment has advanced performance, stable product quality, uniform mixing, and rapid discharging.
Structures & Working Principle
Mixing Tank Structure
The structure of the mixing tank usually includes the tank, mixing device, transmission device, support structure, feed port and discharge port.
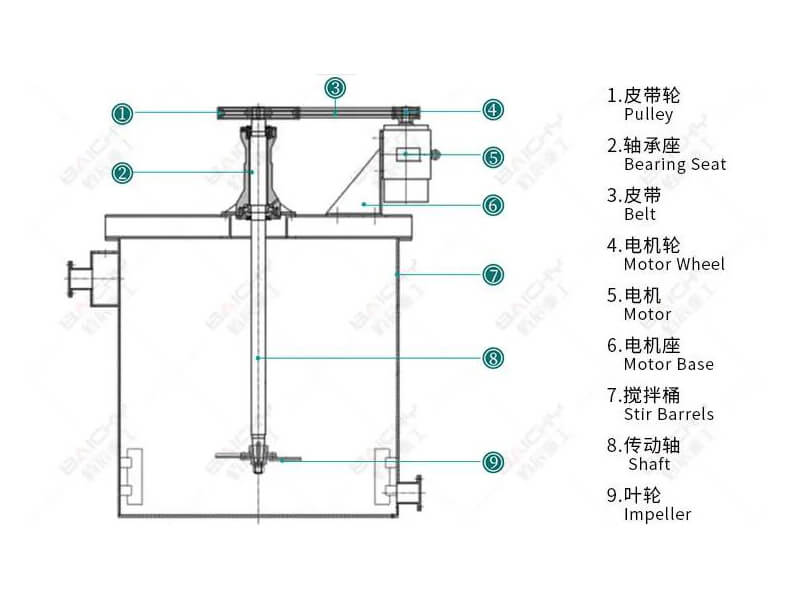
Mixing Tank Working Principle
The slurry and chemical agents are mixed up by the agitator to form ore pulp. Then the pulp is fed to the pulp tank, meanwhile, add air to the pulp, which will form lots of bubbles. The ore particles with hydrophobic properties are attached to the bubbles, and float to the pulp surface, while the ore particles which are hydrophilic stay in the pulp.
The V-belt of the motor drives the impeller to mix chemical agents and slurry completely. The agitator can increase reaction time and strengthen the reaction quality of the chemical agent.
Technical Parameters
| Model | Diameter of Tank(m) | Height(m) | Volume of Tank(m3) | Impeller Diameter(m) | Impeller Speed(r/min) | Power(kw) | Weight(ton) |
| XB1000 | 1 | 1 | 0.58 | 0.24 | 530 | 1.1 | 0.44 |
| XB1500 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 0.4 | 320 | 3 | 1.08 |
| XB2000 | 2 | 2 | 5.46 | 0.55 | 230 | 5.5 | 1.67 |
| XB2500 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 11.2 | 0.65 | 200 | 18.5 | 3.44 |
| XB3000 | 3 | 3 | 19.1 | 0.7 | 210 | 22 | 4.61 |
| XB3500 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 30 | 0.85 | 230 | 30 | 7.28 |










