Lead is a metal element with the symbol Pb and the atomic number 82. It is the non-radioactive element with the largest atomic weight. It is a metal with a higher density than most materials. The lead blocks we see are usually gray-brown. The original color of lead is bluish-white, and the surface will soon be covered by a layer of dark gray basic lead carbonate film in the air.
Lead Features & Uses
The crystal structure of lead is a cubic lattice. Lead has a high density, low hardness, low melting point, high boiling point, corrosion resistance, ductility, poor conductivity of electricity and heat, and can absorb radiation. The above advantages of lead, coupled with the low cost of obtaining lead ore, make it widely used in industries such as chemical, cable, battery, and radiation protection. In addition, it must be mentioned that lead is toxic to the human body. Lead is a heavy metal neurotoxin that accumulates in human soft tissues and bones, which can damage the nervous system and cause nervous system-related diseases.
Main Mineral Types
In nature, there is very little single lead. Lead is mainly mined and refined together with other metals such as zinc and copper. At present, more than 60 minerals are known to contain lead in the world. Galena (PbS lead sulfide) is the main lead-containing mineral, with a lead content of 86.6%. Common lead-containing minerals include cerussite (PbCO3 lead carbonate) and lead alumite (PbSO4 lead sulfate). In addition to common lead-containing minerals, there are also antimonite, brittle antimonite, chrome lead ore, etc.
- Galena (PbS): The primary source of lead, with a high lead content.
- Cerussite (PbCO3): A carbonate mineral with significant lead content.
- Anglesite (PbSO4): A sulfate mineral also rich in lead.
- Jamesonite (Pb4FeSb6S14): Contains lead, iron, and antimony.
- Boulangerite (Pb5Sb4S11): Another lead-antimony sulfide mineral.
- Crocoite (PbCrO4): A rare mineral consisting of lead chromate.
Lead is typically extracted from these minerals through a combination of crushing, grinding, and flotation processes, followed by smelting and refining to obtain pure lead. These deposits are strategically important for various industries, including battery manufacturing, radiation shielding, and construction materials.
Lead Ore Crushing
Lab Jaw Crusher + Roller Crusher Crushing Experiment for Lead-Zinc Ore
Crushing lead ore involves several steps to reduce the size of the raw material to facilitate further processing. Here’s an overview of the process:
Primary Crushing
Jaw Crusher: The primary crusher is typically a jaw crusher, which reduces the large chunks of ore to smaller, more manageable pieces.
Secondary Crushing
Cone Crusher or Impact Crusher: The output from the jaw crusher is fed into a secondary crusher, such as a cone crusher or an impact crusher, to reduce the size of the ore particles further.
Screening
Vibrating Screen: After secondary crushing, the material is screened to separate fine particles from larger ones. The larger particles are sent back to the crusher for further reduction.
Tertiary Crushing
Fine Crushers: For even finer material, tertiary crushers like roll crushers or high-pressure grinding rolls (HPGR) can be used.
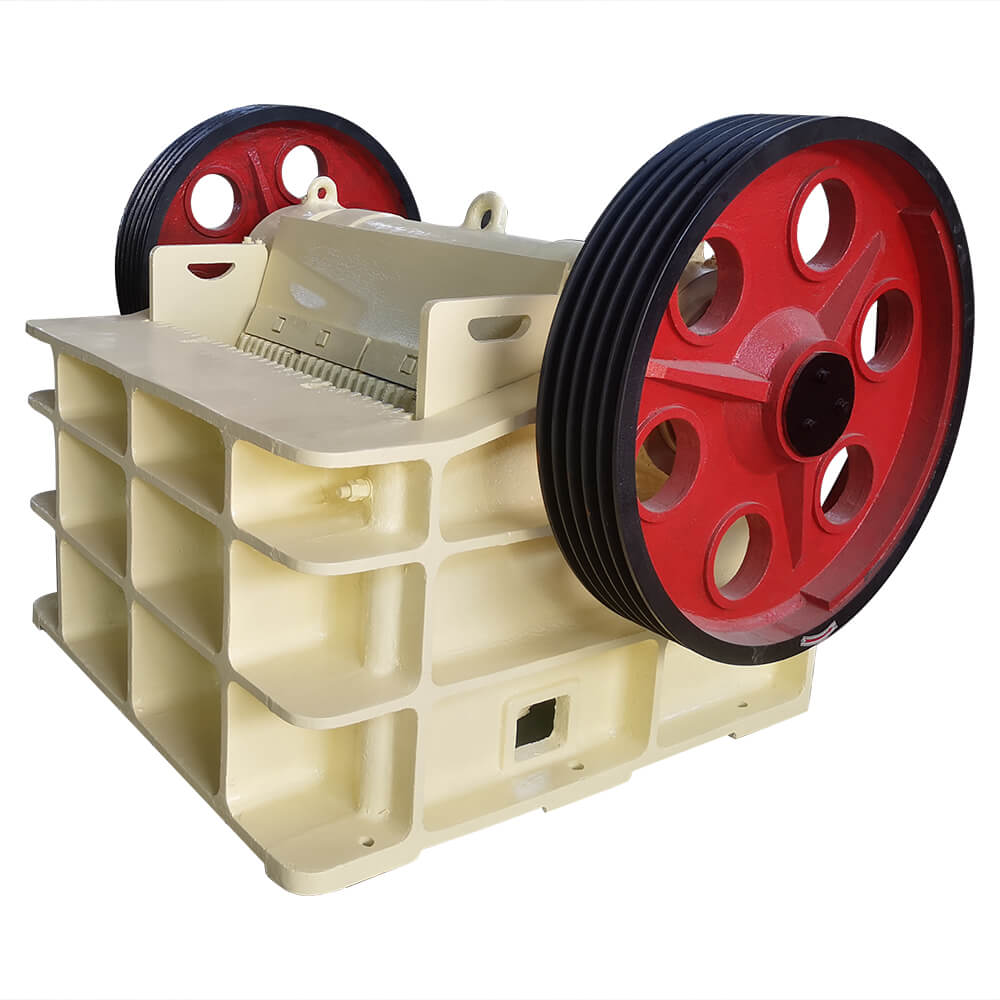
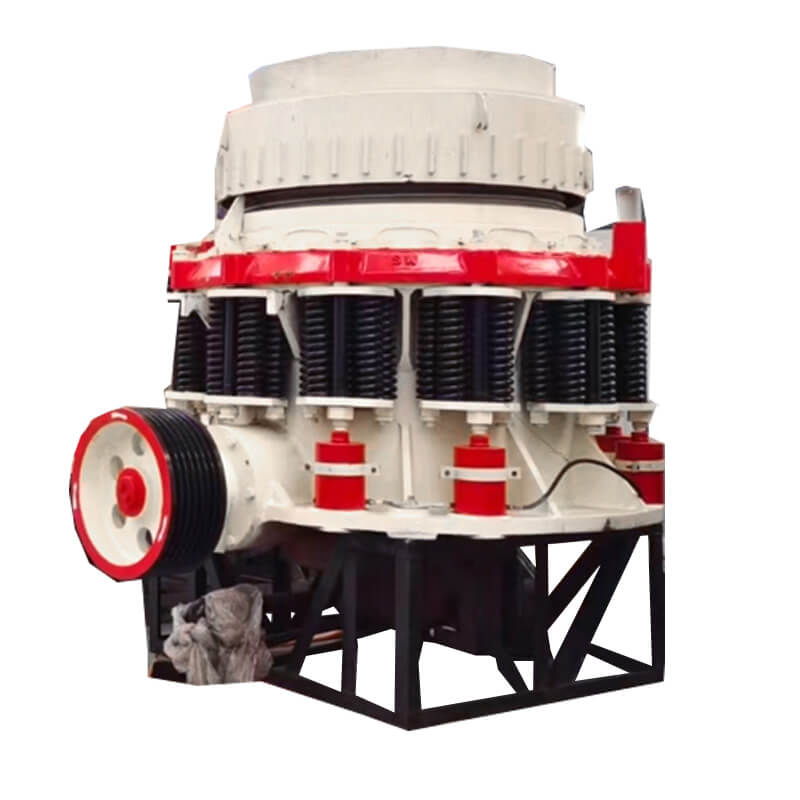
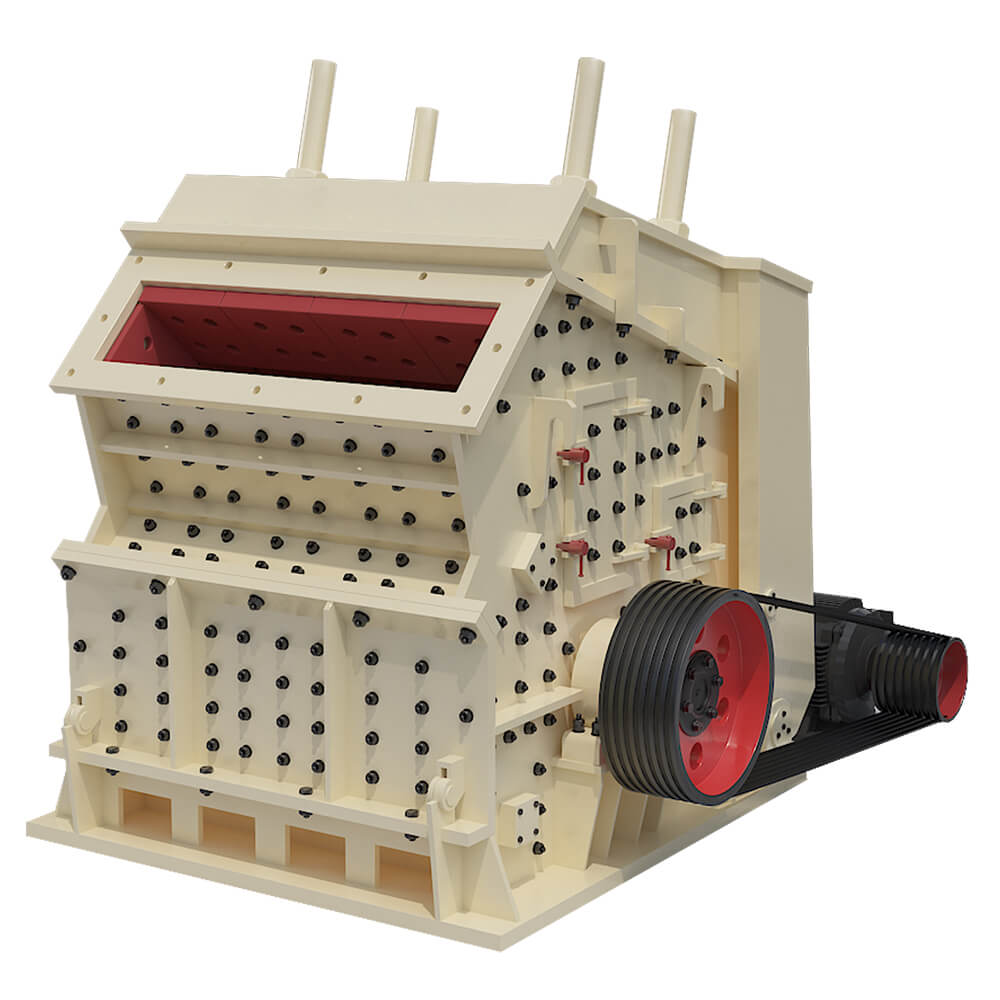
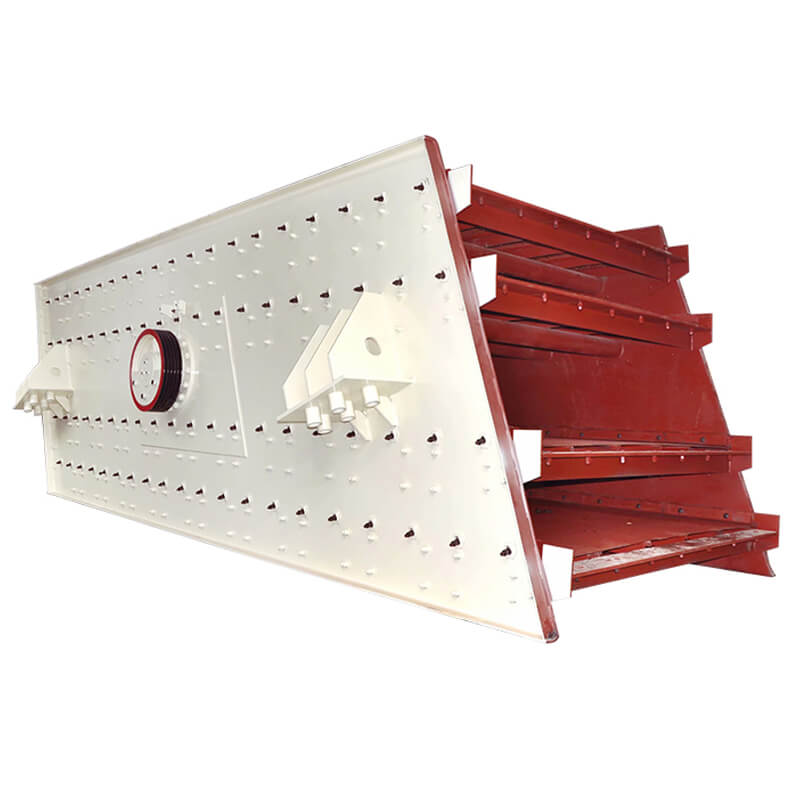




Grinding
Ball Mill or SAG Mill: The crushed ore may then be fed into a grinding mill to reduce the particle size to a powder form.
Separation
Flotation or Gravity Separation: The fine lead ore particles are then subjected to a separation process to concentrate the lead content. Flotation is commonly used for this purpose, where chemicals are added to a slurry of ground ore to selectively adhere to lead particles and float them to the surface for collection.
Concentration and Refinement
Thickening and Filtering: The concentrated lead ore slurry is thickened and filtered to remove excess water.
Smelting: The concentrated ore is then smelted in a furnace to extract lead metal.
Each stage is crucial for the efficient extraction of lead from the ore, ensuring the final product meets the desired quality and purity standards.
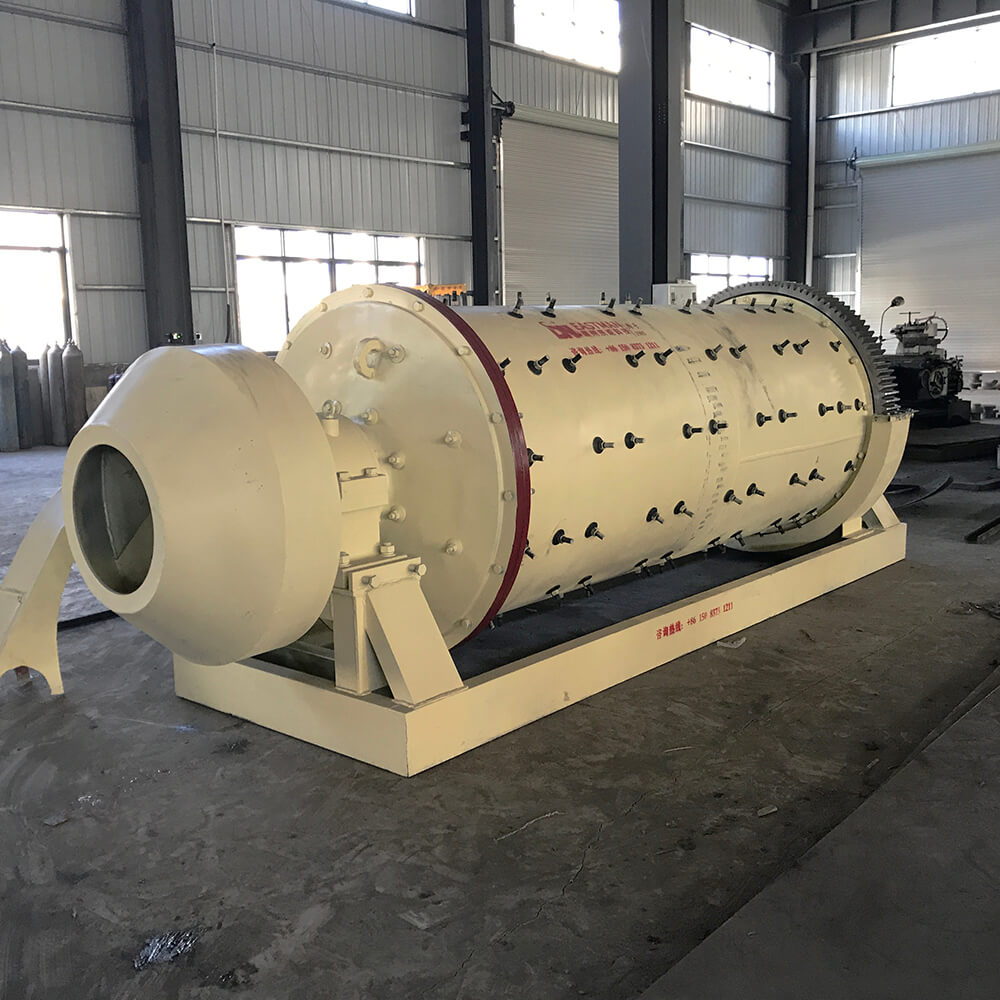
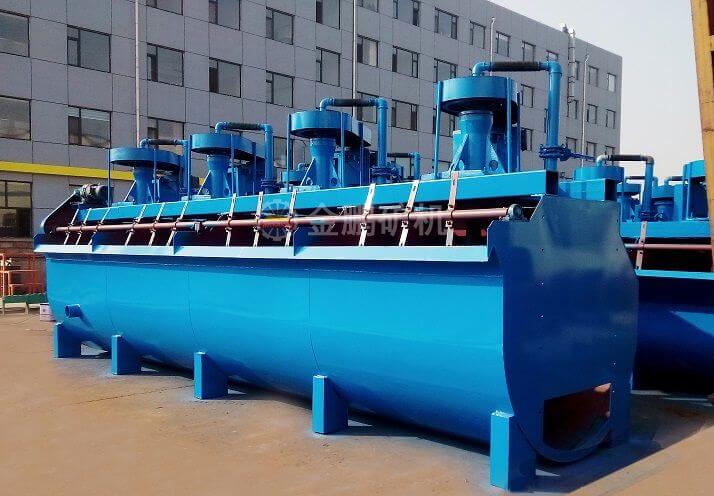
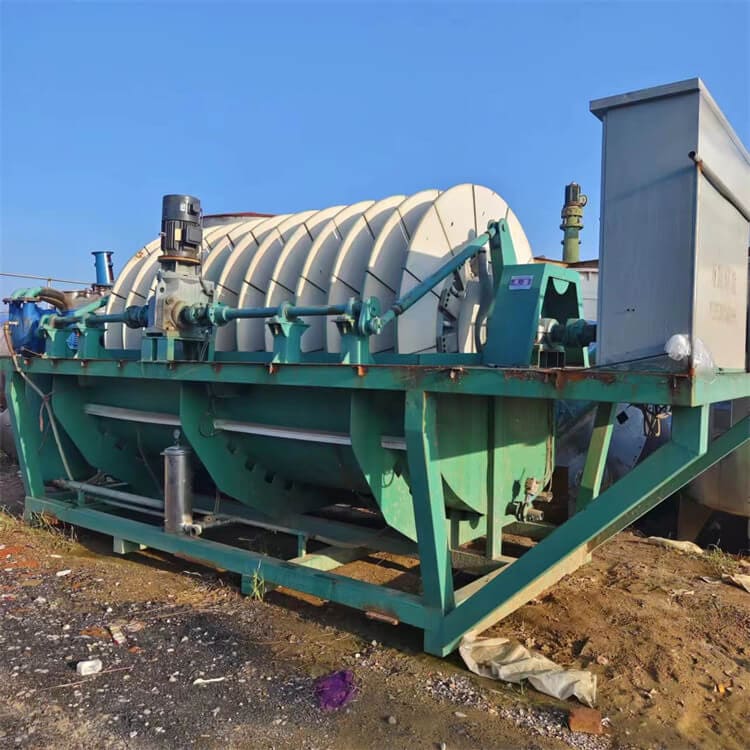




Lead-zinc Ore Production Line
Lead-zinc ore is an important ore source for refining lead. The use of lead-zinc ore for ore dressing generally requires crushing, grinding, and beneficiation. Today, I will introduce to you the overall beneficiation process and crushing production line configuration of lead-zinc ore.
Introduction to lead-zinc ore beneficiation process and beneficiation production line
The beneficiation process of lead-zinc ore includes coarse crushing-grinding-classification-magnetic separation-flotation-concentration-drying and other processes.
The lead-zinc material is first crushed and then sent to the mill for crushing and grinding. The next process is classification. After classification, the lead-zinc mixture is washed and classified, and then magnetically separated. The mineral particles after preliminary separation by the magnetic separator are then sent to the flotation machine. Different flotation agents are added according to the different characteristics of the minerals to separate the desired lead-zinc concentrate from other substances. After the desired concentrate is separated, it must be initially concentrated by the concentrator and then dried by the dryer to obtain a dry and pure finished product.
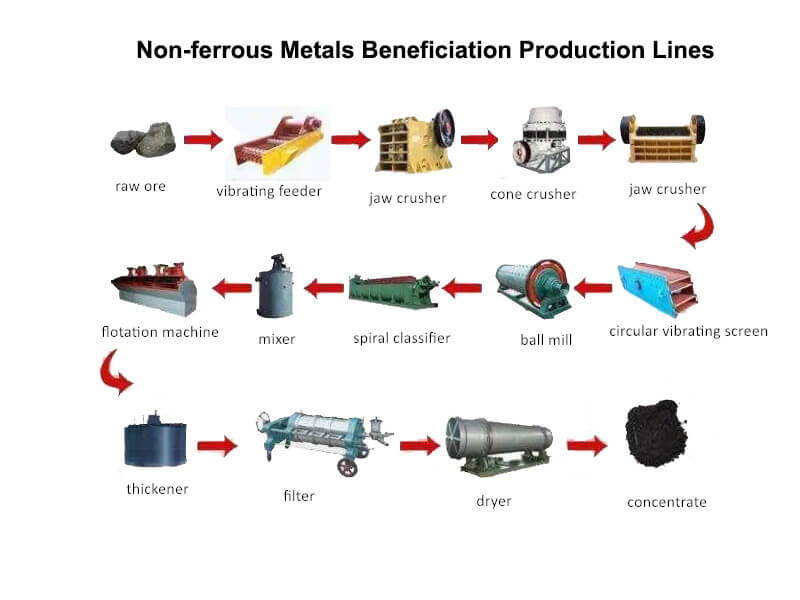
The entire lead-zinc ore dressing production line is composed of jaw crushers, grinding mills, classifiers, magnetic separators, flotation machines, concentrators, and dryers, together with auxiliary equipment such as feeders, elevators, and conveyors.
