Rare earth tailings are waste or by-products produced during rare earth mines’ mining and extraction process. It mainly contains rare earth elements that cannot be extracted from rare earth ores and other non-rare earth components, such as quartz, limestone, etc. Rare earth tailings usually exist in solid or semi-solid form and have complex chemical compositions and physical properties.
Rare earth tailings are formed because the extraction process of rare earth ores is not entirely efficient, or the rare earth elements are not wholly separated during the extraction process, resulting in some rare earths remaining in the waste. In addition, rare earth ores may contain other non-rare earth elements and impurities, which can also form tailings and waste.
Rare Earth Tailinds Recovery
What is Rare Earth Tailings Recovery?
Rare earth tailings recovery refers to treating waste or tailings containing rare earth elements generated from rare earth mines to recover the rare earth elements or convert the waste into usable resources. Rare earth minerals have wide-ranging applications in various fields including, but not limited to:
- Electronic Products: Rare earth elements are used in producing batteries, displays, disk drives, and other critical components of electronic products.
- Magnetic Materials: Rare earth magnets produce permanent magnets for electric vehicle drives and wind turbine generators.
- Optical Devices: Rare earth elements produce lasers, optical communication devices, etc.
- Catalysts: Rare earth catalysts are used to accelerate and control reactions in the chemical industry.
The Importance of Rare Earth Tailings Recovery
Rare earth tailings recycling is significant to the protection and sustainable utilization of rare earth resources, environmental protection, comprehensive utilization of resources, and economic benefits, as shown below.
- Resource protection and sustainable utilization
Rare earth resources are precious strategic resources, and their exploitation is restricted. By recycling unextracted rare earth elements from rare earth tailings, we can minimize the consumption of limited rare earth resources, extend the service life of rare earth resources, and promote the sustainable development and utilization of rare earth resources. - Reduce environmental pollution
Rare earth tailings often contain toxic and harmful substances, such as heavy metals, radioactive elements, etc. If they are directly discharged or piled without treatment, they will easily cause serious pollution to soil, water bodies, and the ecological environment. Recycling and processing rare earth tailings can reduce environmental pollution, and the ecological environment and human health can be protected. - Comprehensive utilization of resources
In addition to rare earth elements, rare earth tailings contain other valuable minerals and components, such as iron, aluminum, calcium, etc. Through the comprehensive utilization of rare earth tailings, rare earth elements can be recovered, and other useful resources can also be obtained, improving resource utilization efficiency. - Economic benefits
Although the rare earth elements contained in rare earth tailings are not completely extracted from the ore, their value is still very high. Recycling unextracted rare earth elements in rare earth tailings can make waste valuable and benefit enterprises economically.
What is The Recycling Value of Rare Earth Tailings?
1. Recycling of metallic iron
During the rare earth tailings stockpiling and treatment process, many iron minerals are carried into the tailings, and the recycling enterprise value is high. The steel concentrator uses strong magnetic medium ore and rare earth flotation production operations, from which we obtain the yield rate of 26.55; iron ore concentrate with a grade of up to 61.65% has an immense recycling value.
2. Recycling of other minerals
Rare earth tailings contain large amounts of rare earth minerals and iron minerals and are rich in valuable components such as barite, sulfur, and niobium. In the combined operation of flotation and magnetic separation, other minerals in the middle are recovered again, with an excellent recovery rate.
3. Application value of rare earth tailings
In addition to the above two critical ways, companies that can effectively recycle rare earth ore tailings can also use grinding mill processing technology to apply it to the building materials industry. In particular, building materials developed using rare earth waste tailings can effectively utilize waste rare earth tailings and improve environmental pollution. They can also significantly enhance the performance of building materials and have great application value.
- In cement manufacturing
Replacing raw clay materials with rare earth tailings can improve the quality of clinker production, enhance the performance of cement materials, and improve mineralization development. - In glass materials
Certain components in rare earth tailings impact the melting and crystallization of glass ceramics and can improve their properties.
Rare Earth Tailings Recycling Methods
Methods for rare earth tailings recovery include, but are not limited to:
- Physical methods
Gravity separation, flotation, and magnetic separation exploit the differences in physical properties of different components in rare earth ores for separation and purification. - Chemical methods
Leaching, solvent extraction, and extraction separation use chemical reactions to extract and separate rare earth elements. - Metallurgical methods
Smelting or refining involves heating or chemical treatment of rare earth tailings to extract rare earth elements.
The processing steps involved in rare earth tailings recovery typically include:
- Ore pretreatment
Pretreatment of rare earth-containing ores involves crushing, grinding, and other processes to facilitate subsequent separation and extraction. - Separation and extraction
Rare earth elements are separated and extracted from tailings using physical, chemical, or metallurgical methods. - Further processing
Extracted rare earth elements are further processed to achieve the desired purity and form. - Waste disposal
Disposal and treatment of waste generated during the processing to minimize environmental impact.
Iron Ore Tailings Recover Rare Earths
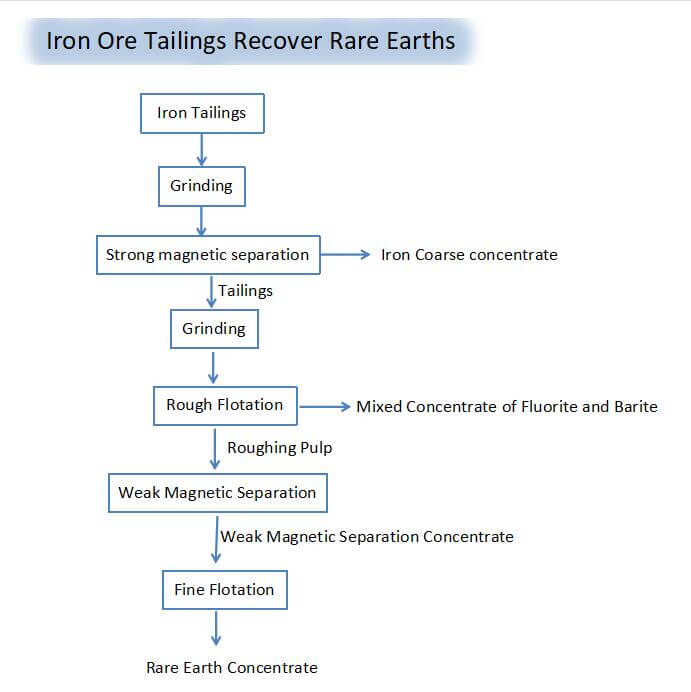
Ore grinding
Grind the iron ore tailings to obtain fine-grained ore, and then add water to the fine-grained ore to prepare slurry I;
Strong magnetic separation
Magnetically separate the ore pulp I to obtain iron coarse concentrate and strong magnetic separation tailings;
Coarse flotation
Grind the strong magnetic separation tailings and add water to prepare slurry II, then add it to the coarse flotation tank for rough flotation to obtain a mixed concentrate of fluorite and barite and a rough slurry;
Weak magnetic separation
Add water to the rough ore slurry to prepare slurry III, adjust the pH value to 5~6, conduct magnetic separation at a temperature of 0~10°C, and obtain a weak magnetic separation concentrate containing rare earth;
Fine flotation
Add water to the weak magnetic separation concentrate to prepare slurry IV, and then add the slurry IV to the fine flotation tank for fine flotation to obtain rare earth concentrate.
The process of this concentrator can effectively separate rare earth concentrates from rare earth tailings and realize the reuse of tailings resources.
