Want to improve your mining operation’s efficiency and profitability? Understanding the differences between differential and bulk flotation is key. Choosing the right method impacts your bottom line. Differential flotation separates valuable minerals and waste from each other. Bulk flotation recovers multiple valuable minerals together. This key difference impacts your processing choices. Choosing the right flotation method isn’t simple. It depends on many factors. Let’s explore each method in more detail.
Table of Contents
What is Differential Flotation?
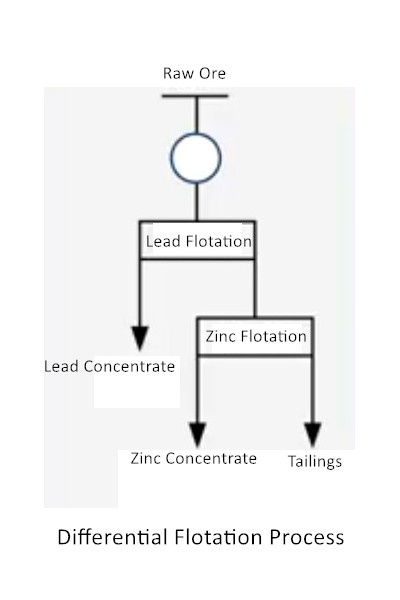
Are you looking for a way to separate valuable minerals from each other, and the waste rock? Differential flotation is a precise process. Differential flotation separates different minerals from a mixture. It uses different reagents. These reagents make specific minerals float. Others sink. This allows for higher-grade concentrates. This also reduces waste!
Definition and Principles
In polymetallic ores, the flotation of different valuable minerals in sequence suppresses others each time. For example, in lead-zinc sulfide ores, zinc is first suppressed to float lead, and then zinc minerals are activated.
Process
Typical as lead-zinc ore: crushing and grinding → lead flotation (inhibitor inhibition of zinc) → zinc activation flotation → tailings treatment.
Applicable conditions
- Sufficient dissociation of minerals.
- Large differences in mineral floatability (e.g., preferential flotation of lead in lead-zinc ores).
- Coarse-grained leached ores (e.g. dense massive sulfide ores).
- High raw ore grade (e.g. Xilin lead-zinc ore).
Advantages and limitations
- Advantages: stable process control, high concentrate grade.
- Limitations: high dosage of inhibitors, high milling cost.
Diving Deeper into Differential Flotation
Differential flotation is complex. It involves multiple steps. Each step uses different reagents and conditions. The goal is to isolate specific minerals. The process requires precise control. This is critical for maximizing recovery and purity. Let’s look at a few key factors:
| Factor | Description | Impact on the Process |
| Reagent Selection | Choosing the right reagents is critical for selectivity. | Determines which minerals float and which minerals sink. |
| pH Control | Maintaining the correct pH is essential for reagent effectiveness. | Impacts the surface chemistry of the minerals. |
| Particle Size | The size of the particles affects flotation performance. | Finer particles may float better than coarser particles. |
| Pulp Density | The concentration of solids in the pulp influences flotation efficiency. | Too much or too little solids can negatively impact recovery. |
| Aeration Rate | The amount of air introduced into the pulp affects the flotation process. | Too much or too little air can hinder effective separation. |
Differential flotation offers many advantages. High-grade concentrates are created. It allows for better recovery of valuable minerals. However, it’s complex and expensive.
What is Bulk Flotation?
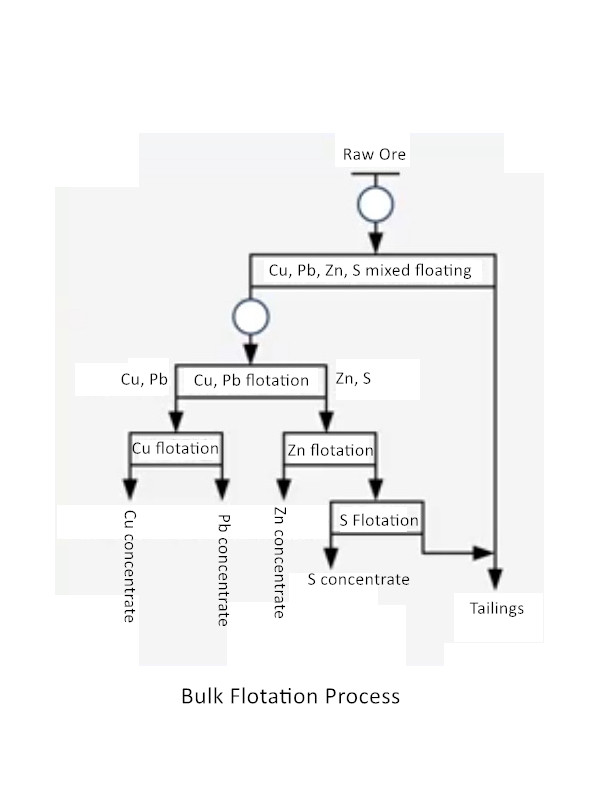
Looking for a way to recover multiple valuable minerals at once? Bulk flotation is a simpler approach. Bulk flotation recovers multiple valuable minerals together. It’s simpler and faster than differential flotation. This makes it cost-effective for some ores.
Definition and Principle
Flotation of all useful minerals into a mixed concentrate first, and then separating them one at a time. For example, copper-lead mixed concentrate is separated into copper concentrate and lead concentrate after regrinding.
Process
Copper and molybdenum bulk flotation: a copper and molybdenum mine adopts “a section of rough grinding – bulk flotation – rough concentrate regrinding – copper and molybdenum and sulfur separation – tailing sulfur separation – copper and molybdenum separation”.
Applicable conditions
- Low-grade ores (e.g. tungsten ore grade <1%).
- Mineral symbiosis close (such as copper-lead sulfide ore).
- Fine-grained embedded ores (reduce over-crushing).
Advantages and limitations
- Advantages: saving milling costs, and reducing equipment investment.
- Limitations: separation difficulties (residual traps in mixed concentrates).
A Closer Look at Bulk Flotation
Bulk flotation is great for ores with multiple valuable minerals. It simplifies the process. This can save on time and costs. It’s a good option when separating individual minerals isn’t crucial. The resulting concentrate still needs further processing. However, this initial step is more efficient. Let’s look at some of its advantages:
Simplicity: Fewer steps mean less equipment and less complex operations.
Cost-effectiveness: Reduced operational costs and higher throughput.
Suitability: This method is ideal for ores with multiple valuable minerals that are easily separated in later stages. However, the concentrate from bulk flotation may contain less valuable minerals. Further processing is necessary to improve grade and purity.
What's The Difference Between Differential And Bulk Flotation?
This is the core question. Understanding the differences will guide your decision-making. The key difference lies in the selectivity and complexity. Differential flotation offers higher selectivity, resulting in purer concentrates, but it is more complex and expensive. Bulk flotation is simpler and cheaper, but it produces a mixed concentrate with lower purity.
Key Differences
| Feature | Differential Flotation | Bulk Flotation |
| Selectivity | High | Low |
| Complexity | High | Low |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Concentrate Purity | High | Low |
| Number of Stages | Multiple | Single or Few |
| Reagent Consumption | High | Low |
Which to Choose Differential or Bulk Flotation For Your Mine?
The best choice depends on your specific circumstances. There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Consider the mineralogy of your ore, the market value of the minerals, and your budget. If your ore contains multiple valuable minerals with significantly different market values, differential flotation is often the better choice. If your ore is simpler and the cost is a major concern, bulk flotation might be more suitable.
Comparative Analysis of Differential And Bulk Flotation
| Indicator | Differential Flotation | Bulk Flotation |
| Applicable ores | High-grade, coarse-grained embedded | Low-grade, fine-grained co-production |
| Pharmaceutical consumption | High inhibitor/activator usage | Concentrated collector usage but complex separation stage |
| Economic Benefits | High concentrate quality but high cost | Low initial costs but increased separation costs |
| Typical cases | Fankou lead-zinc ore (preferential lead flotation) | Copper-molybdenum ore (mixed flotation followed by separation) |
Think of it like this. If you’re mining a complex ore with valuable minerals like gold and copper, differential flotation allows you to extract both efficiently, maximizing your return. However, if you’re dealing with a simpler ore containing mostly copper, bulk flotation might be the more economical option. Remember to factor in the potential need for further processing if you choose bulk flotation. Sometimes, a combination of bulk and differential flotation can be the most efficient solution. This approach can optimize both recovery and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
Differential and bulk flotation are both important mineral processing techniques. The best choice depends on specific needs. A thorough evaluation of factors will determine the most appropriate method. Consider ore characteristics, processing costs, and environmental regulations when making your decision. This decision directly impacts your mine’s profitability.
